Loading library...
Processes - Plating
Plating
Plating is a surface treatment process where a thin metal layer is deposited over a substrate to provide corrosion resistance, enhance appearance, offer wear protection, or improve electrical conductivity. Electroplating involves the use of an electric current, whereas electroless plating uses a chemical reduction reaction. Both techniques have significant applications in electronics, aerospace, automobiles, and decoration.
Process Cycle
- Pre-cleaning (degrease, ultrasonic, acid dip)
- Surface activation and washing
- Metal deposition (autocatalytic for electroless, electrochemical for electroplating)
- Post-treatment (drying, passivation, rinsing)
- Quality inspection (thickness, adhesion, finish)
Equipment
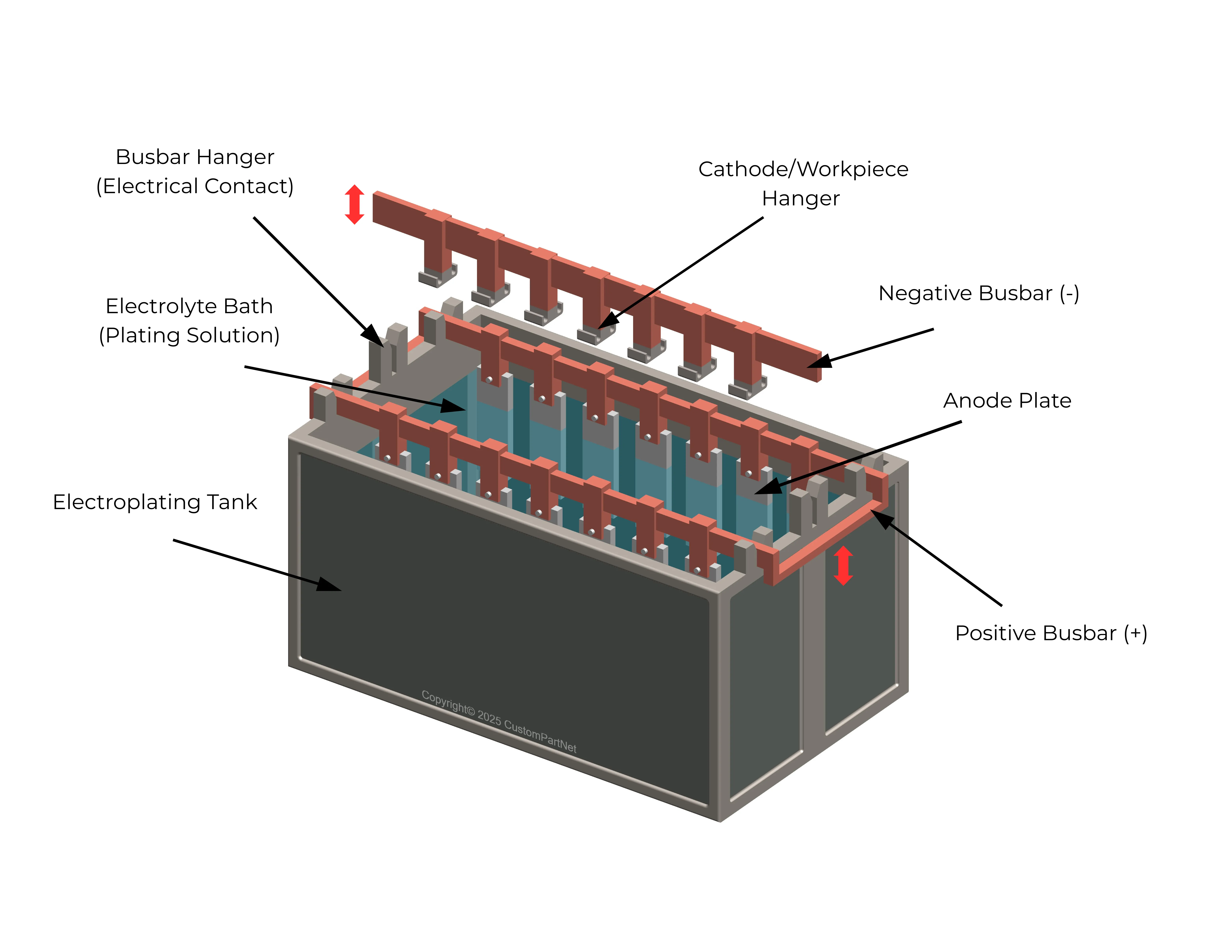
- Electroplating tanks with rectifiers (DC power supply)
- Anode and cathode fixtures
- Agitation systems (mechanical or air)
- Temperature and pH control systems
- Filtration and chemical dosing units
- Spray and immersion rinse stations
Tooling
Primary:
- Part handling barrel or rack fixtures
- Selective masking plating systems
Secondary:
- Thickness measuring equipment (XRF, coulometry)
- Repeatability inspection fixtures
- Surface conditioning brushes or polishing wheels
Materials
| Plating Metal | Substrate Compatibility | Properties Enhanced |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel | Steel, Copper, Plastics | Wear resistance, solderability |
| Chromium | Steel, Brass | Hardness, corrosion resistance |
| Zinc | Steel | Sacrificial corrosion protection |
| Gold/Silver | Copper, PCB tracks | Electrical conductivity, aesthetics |
| Tin | Copper, Aluminum | Solderability, corrosion resistance |
Possible Defects
- Uneven thickness or inadequate coverage
- Delamination or peeling
- Pitting and porosity
- Overplated or burnt areas
- Poor discoloration due to improper rinsing
- Contamination due to improper bath maintenance
Design Guidelines
- Prevent re-entrant corners or recesses (produces uneven plating)
- Provide an even path of current in electroplating designs
- Use drain holes for internal cavities
- Use masking to limit areas of plating
- Provide dimensional growth tolerance stack-up
Cost Drivers
- Plating metal type and thickness
- Part surface area and geometry
- Batch size and masking complexity
- Process type (manual vs. automated)
- Chemical use and disposal cost
Plating imbues significant value in components by maximizing both functional and aesthetic features. Designed fixtures, bath chemistry control, and pre-treatment procedures imbue consistency and efficiency in industrial plating processing.